The immune system plays a crucial role in the human body. The immunity system not just stands tall against injuries, instead it acts as a wall against a range of infections, chronic diseases, and acute diseases. However, the body's defenses may be ineffective against cancerous or tumor cells. White blood cells, of which lymphocytes are a component, number in the billions in the immune system. The majority of white blood cells are made up of lymphocytes, which fall under the following categories:
- B Lymphocytes- Also known as B-cells, make antibodies to fight infection
- T Lymphocytes- Also known as T-cells, kill the infected cells in the body and assist B-cells in making antibodies to fight infection
- Natural Killer Cells- They eliminate viruses and attack infected cells in the body
Immunotherapy, a concept gaining popularity globally, is increasingly being used against cancer. Immunotherapy is a treatment that uses the ‘body’s very own immune system and strengthens it against cancer. Immunotherapy 'increases the body’s ability to detect and kill cancer cells.
In a laboratory setting with strict controls, immune cells or antibodies can be created and subsequently administered to patients to cure cancer. To find out which types of immunotherapy are most effective in treating specific cancers, several have either received approval for usage or are currently being investigated in clinical trials.
Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-Cell Therapy
Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-T cell therapy is a method for treating specific types of blood malignancies that use your immune system to attack cancer. With CAR-T cell treatment, immune cells called T cells are taken out of the blood and given a new gene that makes them capable of identifying cancer. The T cells are injected back into the circulation once the gene has been added, where they multiply and start a range of immunological reactions meant to kill the cancer cells.
Adult and pediatric leukemia, as well as some forms of lymphoma, are all treated using CAR-T cell therapy. Additionally, it is being researched as a potential treatment for many solid tumors that develop in the chest and other malignancies. But how does it work?
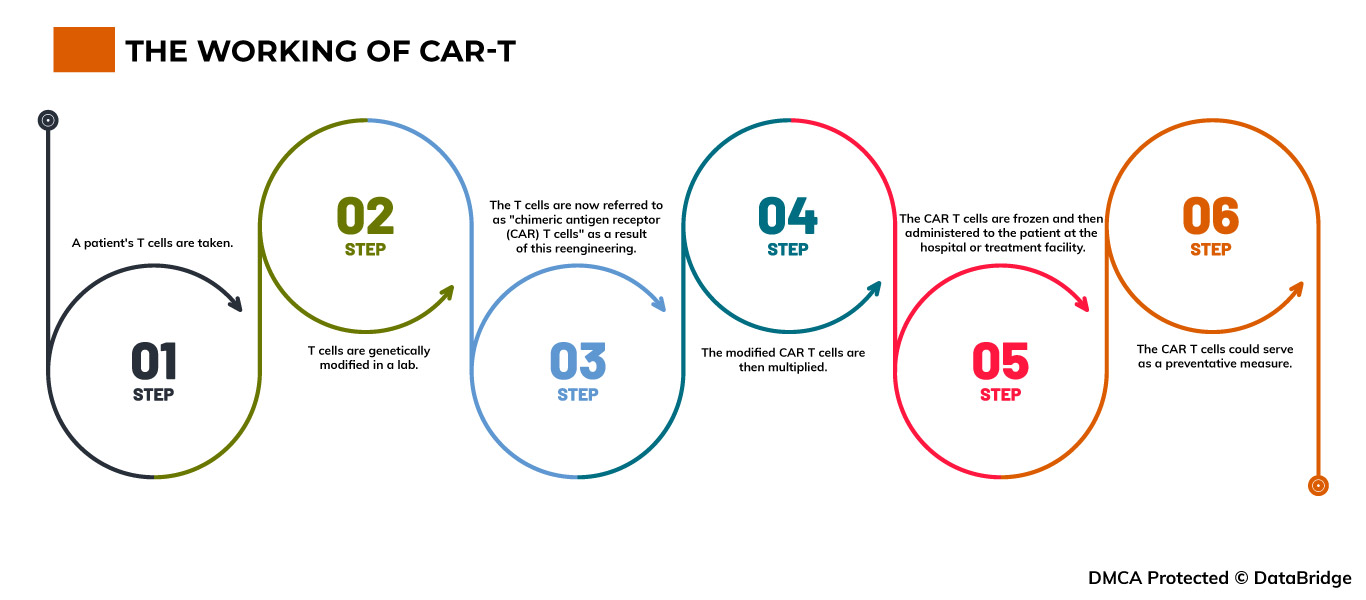
Fig.1: The working of CAR-T
Step 1- A patient's T cells are taken. T cells are obtained through the process of apheresis, which involves drawing blood from the body and removing one or more blood components (such as plasma, platelets, or white blood cells). The body is then given the remaining blood.
Step 2- T cells are genetically modified in a lab. The T cells are delivered to a lab or a pharmaceutical manufacturing facility, where they are genetically modified by inserting DNA to create chimeric antigen receptors (CARs) on their surface.
Step 3- The T cells are now referred to as "chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells" as a result of this reengineering. The T cells can recognize an antigen in specific tumor cells thanks to CARs, which are proteins.
Step 4- The modified CAR T cells are then multiplied. By cultivating cells in a lab, the quantity of the patient's genetically altered T cells is "expanded". Once there are sufficient numbers, these CAR T cells are frozen and delivered to the medical facility or facility where the patient is receiving treatment.
Step 5- The CAR T cells are frozen and then administered to the patient at the hospital or treatment facility. Before receiving the infusion of CAR T cells, many patients undergo a brief course of one or more chemotherapy drugs, referred to as "lymphodepletion." The number of CAR T cells that have been reintroduced into the patient's bloodstream increases. These "attacker" cells will detect cells with the specific antigen on their surface and attack them.
Step 6- The CAR T cells could serve as a preventative measure. All cancer cells may be eliminated by CAR T cells, which may stay in the body for months after the infusion. Some forms of blood cancer have experienced prolonged remissions as a result of the treatment.
The CAR-T cell therapy treatment market is expected to gain market growth in the forecast period of 2021 to 2028. Data Bridge Market Research analyses that the market is growing with a CAGR of 30.0% in the forecast period of 2021 to 2028 and is expected to reach USD 37,423.56 million by 2028. Increase in usage of CAR-T cell therapy for the treatment of cancer and infectious disease acting as driver for the CAR-T cell therapy treatment market growth. Japan is leading the growth of the Asia-Pacific CAR-T cell therapy treatment market. The autologous CAR-T cells segment is dominating in the country due to increased research regarding CAR-T cell therapy treatment. The autologous CAR-T cells segment in Germany is dominating the Europe CAR-T cell therapy treatment market owing to prevalence of cancer.
To know more about the study, visit: https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-car-t-cell-therapy-treatment-market
Approved CAR-T Cell Therapies
For indications or tumors other than those for which the FDA has approved it, CAR T-cell therapy is still accessible to patients who are taking part in a clinical trial. Trial procedures differ. Care may be given in a hospital setting or an intensive outpatient treatment facility with knowledge of providing cellular immunotherapy, depending on the clinical trial.
Before, during, or after treatment, patients may be required to stay at the treatment center or make arrangements to do so. Before individuals can sign up for a trial, several trial procedures demand that patients confirm the availability of a caregiver. The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has given the green light for CAR T-cell treatments to treat certain leukemia, lymphomas, and multiple myeloma cases. After alternative forms of treatment have been exhausted, CAR T-cell therapy is frequently used. Current approved CAR T-cell therapy examples include:
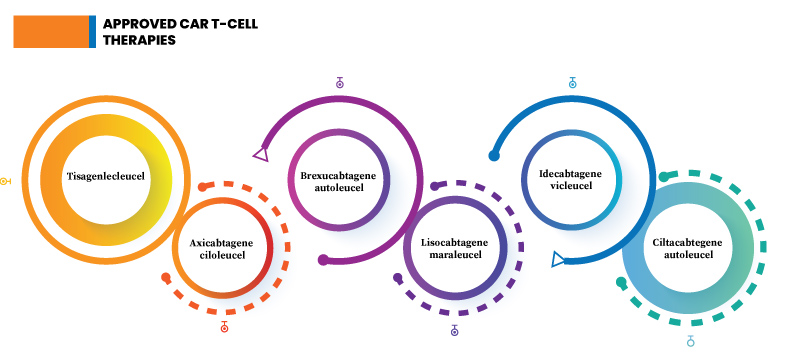
Fig.2: Approved CAR T-cell therapies
Tisagenlecleucel- Also known as tisa-cel (Kymriah), it is used to treat B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma, including diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), follicular lymphoma with DLBCL, and high-grade B-cell lymphoma.
Axicabtagene Ciloleucel- Popularly known as axi-cel, this immunotherapy is used against primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma.
Brexucabtagene Autoleucel- Popularly known as brexu-cel, this immunotherapy is used against B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL). B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) affects the immature B lymphocytes in the WBCs.
Lisocabtagene Maraleucel- Also known as liso-cel, it is used to treat B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL).
Idecabtagene Vicleucel- Also called ide-cel, is used against mantle cell lymphoma.
Ciltacabtegene Autoleucel- Also called cilta-cel, it is used against multiple myeloma
Common and Possible Side Effects of CAR-T Cell Immunotherapy
CAR T-cell therapy can be very effective in treating some difficult-to-treat cancers, but it can also have serious or even life-threatening side effects. As a result, it must be administered in a medical facility that has been specially trained in its use, and patients must be closely monitored for several weeks after receiving the CAR T cells. CAR T-cell therapy, such as most cancer treatments, has side effects that can sometimes be life-threatening. Cytokine release syndrome and neurological problems are the two most common side effects.
Cytokine Release Syndrome- Cytokine release syndrome (CRS) can occur after your CAR T-cells begin multiplying and attacking cancer cells. Cytokines are chemicals that stimulate the immune system. When your CAR T-cells begin to function, your immune system may respond by releasing large quantities of cytokines into your bloodstream. CRS usually occurs within the first week or two of treatment. Common symptoms of an individual suffering from are:
- Flu
- High fever and chills
- Nausea, vomiting and diarrhea
- Dizziness
- High blood pressure
- Fast heart rate
- Tiredness
Neurological Problems- CAR T-cell therapy can affect your nervous system, causing symptoms in the first few weeks after treatment. Because some symptoms can impair your ability to drive or operate machinery, you should avoid doing so for at least eight weeks after treatment. Common side effects under this include:
- Headaches
- Seizures
- Confusion and agitation
- Tremors and twitching
- Balancing confusion and problems
- Speaking difficulty
Some CAR T-cell therapies may increase your risk of infection. CAR T-cells are designed to recognize a protein called CD 19 and are used to treat some leukemia and lymphomas. Most B cells have CD 19 on their surface. B cells are a type of white blood cell that, like T cells, play an important role in infection resistance. CAR T-cell therapy that targets the CD 19 protein also kills B cells. It kills both normal and cancerous B cells. This either reduces or eliminates the number of B cells. This makes fighting infections more difficult. This side effect may necessitate medical attention. This is known as immunoglobulin therapy.
This can happen when CAR T-cell therapy rapidly breaks down a large number of cancer cells. As the cancer cells degrade, they release uric acid into the bloodstream. The kidneys struggle to cope with high uric acid levels. Regular blood tests are performed to check for this. If you develop tumor lysis syndrome, you will be given fluids into your vein and medication to help lower uric acid levels in your blood.
Most patients require hospitalization for a week to ten days so that their healthcare providers can monitor their response to the treatment and treat any side effects. You might be able to get your CAR T-cells without having to stay in the hospital.
Failure of CAR-T Cell Therapy: Cases/ Situations
CAR T-cell therapy is not without flaws. CAR T-cell therapy does not always kill cancer cells as expected. Sometimes the treatment is effective, but the cancer returns. Some of the reasons why CAR T-cell therapy may fail include:
- CAR T-cells are T-cells that have received new genetic instructions, allowing them to produce chimeric antigen receptors (CAR) and molecules. T-cells must activate or start up the new receptors in order for them to find and kill cancers. CAR T-cells cannot function unless this occurs.
- CAR T-cells are supposed to multiply once they enter your body. If they do not, they may not find and kill enough cancer cells to prevent cancer from spreading.
- CAR T-cells can sometimes simply stop killing cancer cells. T-cell exhaustion occurs when this occurs. T-cell exhaustion, according to researchers, may be linked to proteins known as transcription factors, which help turn genes on and off.
- Cancer cells can change or mutate, causing the CAR T-cells to lose the antigen they were designed to detect.
Prognosis and Future Outlook of CAR-T Cell Therapy
CAR T-cell treatment is still in its infancy, but trials continue to show promising outcomes. For instance, research conducted in 2020 followed kids with acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL). After treatment, more than 85% of children with ALL went into complete remission, and 60% of those kids were still cancer-free a year later. Additionally, scientists are working hard to gain a fresh understanding of CAR T-cell treatment. CAR T-cell was the subject of more than 800 investigations as of March 2020. Current research examples include:
- Examine CAR T-cell therapy's potential to treat solid tumor malignancies such as breast and lung cancer.
- Finding strategies to lessen the side effects of therapy.
- Looking at ways to prolong the period when CAR T-cells can contain malignancy.
- Looking for ways to increase the production of CAR T cells so that patients can receive treatment more quickly.
Data Bridge Market Research analyses that the chimeric antigen receptor T (CAR-T) cells market which was USD 1,965.8 million in 2021, would rocket up to USD 28714.00 million by 2029, and is expected to undergo a CAGR of 39.82% during the forecast period 2022 to 2029. The rise in the frequency of cancer, the increase in the number of patients who have failed to respond to alternative treatments, and the rise in healthcare costs are all predicted to promote the growth of the chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-T cell therapy market in the forecast period. In July 2020, after getting FDA permission for commercialization in the United States, Kite Pharma, a Gilead Sciences subsidiary, introduced Tecartus.
To know more about the study, visit: https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-chimeric-antigen-receptor-t-car-t-cells-market









