OVERVIEW:
Fisheries and aquaculture is the process of cultivating saltwater and freshwater populations which include fish, aquatic plants, algae, shellfish, molluscs, crustaceans, and other populations found in the water environment. Fisheries and aquaculture play an important role in the development of the economy. According to FAO, the global demand for fish and fish products has never shown signs of slowing down and the sector has expanded at a very faster rate over the past decade. According to FAO, major facts related to fisheries and aquaculture include.
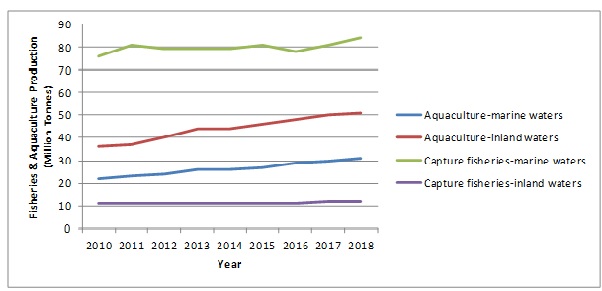
- In 2018, the fisheries recorded the highest production of 96.4 million tonnes which was 5.4% higher than the average of the past three years
- Global aquaculture production experienced a growth of 527% from 1990 to 2018
- Global fish consumption experienced growth of 122% from 1990 to 2018
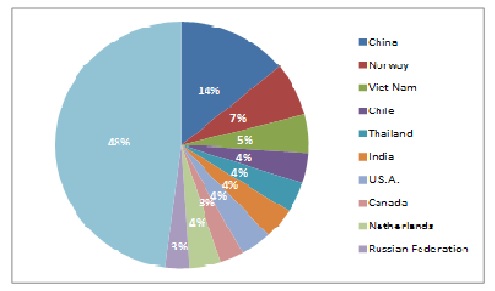
- The top capture producers in 2018 include China, Indonesia, Peru, India, the Russian Federation, the United States of America, and Vietnam. These countries account for 50 % of total global capture production
- In 2018, the world aquaculture production was 114.5 million tonnes with a sales value of USD 263.6 billion
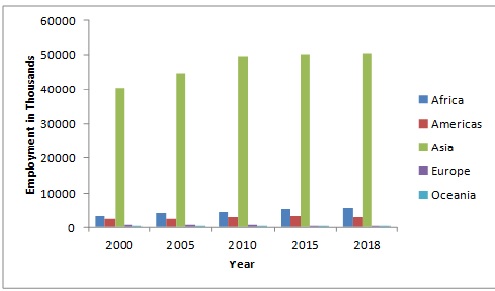
- Fisheries and aquaculture is an important source of employment. In 2018, around 59.5 million people were engaged in this field. 39.0 million people were employed in fisheries and 20.5 million people were employed in aquaculture
World Capture Fisheries and Aquaculture Production (Million Tonnes)
 World Employment for Fishers and Fish Farmers, By Region
World Employment for Fishers and Fish Farmers, By Region
 Fish Trade and Products
Fish Trade and Products
According to FAO, in 2018, 67 million tonnes of fish and fish products were traded with total export value of USD 164 billion. Top exporters include China, Norway, Vietnam, Chile, Thailand, India, U.S., Canada, the Netherlands and Russian Federation among others.
Top Exporters of Fish and Fish Products In Terms Of Value, 2018
 The above statistics shows that fisheries and aquaculture play an important role for the economic development of any country, but the COVID-19 pandemic is creating an economic crisis in fisheries and aquaculture owing to various measures taken by countries to restrict the rate of infection such as business closures, home confinement, and travel bans. The fisheries and aquaculture industry is subjected to indirect impacts of the COVID-19 through logistical or market access problems related to border and transportation restrictions, changing consumer demands. This is expected to have a major impact on fish farmers and fishers' livelihoods, as well as on food security and nutrition for peoples largely depending on fish for protein requirement and essential micronutrients.
The above statistics shows that fisheries and aquaculture play an important role for the economic development of any country, but the COVID-19 pandemic is creating an economic crisis in fisheries and aquaculture owing to various measures taken by countries to restrict the rate of infection such as business closures, home confinement, and travel bans. The fisheries and aquaculture industry is subjected to indirect impacts of the COVID-19 through logistical or market access problems related to border and transportation restrictions, changing consumer demands. This is expected to have a major impact on fish farmers and fishers' livelihoods, as well as on food security and nutrition for peoples largely depending on fish for protein requirement and essential micronutrients.
THE IMPACT OF COVID-19
The dynamics and nature of COVID-19 impacts are manifold. Economically, the International Monetary Fund (IMF) projected that the global GDP is expected to decrease by 3% in 2020 from 2.9% growth in 2019. Asia which is the largest producer of fisheries and aquaculture is also expected to have COVID-19 impact. According to, the Asian Development Bank (ADB), the growth in developing Asia will be 2.2% in 2020 which was 5.5% before the COVID-19 pandemic. This slowdown is expected to lead to widespread unemployment, food insecurity, and exacerbation of social inequities.
Fish products and fish are an important component of a healthy diet and are safe to eat. Fishes are not responsible for an epidemiological role in spreading COVID-19 to humans. But, people misleading perceptions in some countries about fish and the spread of COVID-19 have to lead to decreased consumption of fish products.
There was an immediate impact on the aquaculture business. Lockdowns subjected the value chain to certain international and domestic transport disruptions for raw materials for processing, production inputs, and finished products for export and domestic consumption. Strict imposition of restrictions on the movement of people and materials including workers, farm-made inputs such as seed, feed, unavailable. Small fish farmers experienced a business loss because they had to sell the products at lower prices or could not sell their harvests. Due to lockdown in the majority of the countries, fish farmers were not able to harvest and also could not start a new production cycle resulting in reduced fish supply in the next few months and also loss of downstream and upstream sources of employment.
The export of fish of major countries such as China and the EU were affected to lockdown. The closures of schools and offices also impacted the demand for fresh fish and they are relying on prepared meals. The shutdown of restaurants and hotels has also decreased the demand for live and fresh high-value fish. E-commerce has helped to offer the products, but sales are still lower than pre-pandemic.
Closures of offices and schools have also affected the demand for fresh fish. The busy lifestyle of people in urban centers makes them rely on prepared meals. These meals often include fish products and are served by small vendors and restaurants for take-away or on-site consumption. The shutdown of tourism and related businesses, such as hotels and restaurants, has also decreased demand, especially for high-value fresh or live fish. E-commerce has helped absorb the products, but sales are still far lower than before the pandemic.
IMPACT ON FISHERIES AND AQUACULTURE SUPPLY CHAIN
The activities needed to deliver fishery and fish products from production to the final consumer are complex. The technologies used differ across the world from artisanal to highly industrial. The value chains include global, regional, and local markets. The key activities in the supply chain of aquaculture or fisheries include aquaculture production, fishing, transport, processing, and retail & wholesale marketing. Each activity in the supply chain has disrupted owing to the impacts of COVID-19 which is affecting the sector's economy.
Fishing:
Unavailability of supplies such as gear, ice, and bait due to the shutdown or not able to provide inputs on credit is also restricting the fishing activity. Labour shortage because of restrictions on transportation is affecting the fishing activity.
Aquaculture Production:
Fish farmers are not able to sell their harvest due to the market disruptions and therefore they are keeping huge quantities of live fish which is needed to be supplied for an indeterminate period increasing costs, expenditure, and risks. The export of farmed species such as pangasius is affecting owing to the closure of international markets. Aquaculture is being mainly affected owing to the closure of restaurants and hotels. These factors are leading to a decrease in the production of fisheries and aquaculture.
Processors:
The fisheries and aquaculture are mainly depending on the foodservice sector which is being majorly affected by changes in food services. Due to the implementation of lockdown in various countries across the world the restaurants, hotels, and canteens are closed down resulting in the reduction of activities of fish wholesalers. The raw material for frozen, pre-packed, and canned fish and fish products is also not available because of logistical issues. Due to the barriers to transportation or delayed transportation the products are being subjected to loss, quality change, and additional costs for exporters, processors, traders, and importers.
Difficulties Related to Working Conditions Along the Value Chain:
The fishing crew is unable to travel from home due to restrictions on flights and quarantine periods. The COVID-19 virus may spread rapidly among the crew members and medical assistance may not be readily available. Most of the fishers have migratory nature and also international visitors frequently visit fishing communities which may increase the risk of spread of COVID-19 which are creating difficulties for crew members.
COPING STRATEGIES AND SUPPORT TO THE SECTOR BY MAJOR FISH AND AQUACULTURE PRODUCING COUNTRIES
- The government of China has launched the National Fish Demand and Supply Information Platform under the Authority of the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs. This has helped many small-scale enterprises and leading companies to sell their products through this platform
- In India, a community radio station has been launched which is acting as a bridge between fishers and government. The station invites doctors, municipal staff, and police officers to respond to concerns and questions from fishers about the pandemic
- In Indonesia, fishers are depending on other species as a replacement to blue swimming crab for export. The alternatives include shrimp, squid, and mixed finish species.
- In the Philippines, the Department of Agriculture has launched the Food Lane Conduct Pass to ensure uninterrupted flow and supply of agriculture, food commodities, and fishery products
INITIATIVES TAKEN BY FISHERIES AND AQUACULTURE COMPANIES FOR COVID-19
The aquaculture and fisheries are a major part of the global food system and hugely nutritious food group of major cultural, social, and economic importance. The industry is already facing difficulties in supply chains for aquatic and fish foods owing to disruptions in trade, transportation, and labor. Decreased production from reduced fishing efforts and extended stocking of aquaculture systems will create reduced access, supplies, and consumption of these foods. Increased transaction costs and decreased demand from the consumer end will have an impact on the prices of aquatic and fish products, to address these impacts, the manufactures in this industry are taking some initiatives,
For instance,
"Our priority is the health and safety of our employees who are doing essential work supplying food to families across North America. We are maximizing all available resources to safeguard our people and ensure a steady supply of frozen seafood to meet the needs of retailers and consumers across North America during this unprecedented time."
- Rod Hepponstall, President and Chief Executive Officer of High Liner Foods
“COVID-19 has created a positive movement for us, where many customers who would have taken several years to switch to hygiene meat/seafood brand are happening faster now. This is an opportunity at the time of crisis. The COVID-19 spread is very sensitive; hence we have taken utmost precaution in our stores and for the delivery partners by implementing many new SOPs to keep them safe. We have also introduced Contactless Retail service for our customers recently. Under the same, a customer can download the TenderCuts app, place the order and the company will allot a time slot for the customer to pick up the order from the store. Once the customer arrives at the store, they can sanitize themselves and the product will be kept ready which will allow the customer to complete his retail experience in a matter of few minutes. Online payment for the order is mandatory for the customers to make the service a seamless and safe experience.”
-Nishanth Chandran, Founder and CEO for Tendercuts
“Given global pandemic challenges, Cooke Aquaculture decided it was appropriate to defer our RAS smolt facility in Chile until the situation improves. At this time, our focus remains on taking all reasonable steps to protect our people and maintaining our current operations to serve customers.”
-Joel Richardson, Communications chief for Cooke Aquaculture
“As an organization, we began to address the COVID-19 pandemic on March 2, 2020, through changes to our policies and procedures. These changes are in support of recommendations made by federal and provincial governments and health authorities, and are intended to further protect our employees and support their ongoing health and wellbeing. We will continue to monitor and make changes as required to ensure the safety of our employees, our contractors and suppliers and the community”
-David Kiemele, Managing Director for Cermaq Canada
Conclusion:
Fisheries and aquaculture are a crucial industry in the economic development of major fish and aquaculture producing countries. Post pandemic the industry was growing rapidly without showing any signs of slowing down, but due to the economic barriers imposed by various countries across the world, the industry is expected to see a decline in the growth for the next few months owing to the reduced production.




 World Employment for Fishers and Fish Farmers, By Region
World Employment for Fishers and Fish Farmers, By Region Fish Trade and Products
Fish Trade and Products The above statistics shows that fisheries and
The above statistics shows that fisheries and